We’ve found that certain search terms are good indicators of flu activity. Google Flu Trends uses aggregated Google search data to estimate flu activity in your state up to two weeks faster than traditional flu surveillance systems.
Each week, millions of users around the world search for online health information. As you might expect, there are more flu-related searches during flu season, more allergy-related searches during allergy season, and more sunburn-related searches during the summer. You can explore all of these phenomena using Google Trends. But can search query trends provide an accurate, reliable model of real-world phenomena?
We have found a close relationship between how many people search for flu-related topics and how many people actually have flu symptoms. Of course, not every person who searches for “flu” is actually sick, but a pattern emerges when all the flu-related search queries from each state and region are added together. We compared our query counts with data from a surveillance system managed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and discovered that some search queries tend to be popular exactly when flu season is happening. By counting how often we see these search queries, we can estimate how much flu is circulating in various regions of the United States.
During the 2007-2008 flu season, an early version of Google Flu Trends was used to share results each week with the Epidemiology and Prevention Branch of the Influenza Division at CDC. Across each of the nine surveillance regions of the United States, we were able to accurately estimate current flu levels one to two weeks faster than published CDC reports.
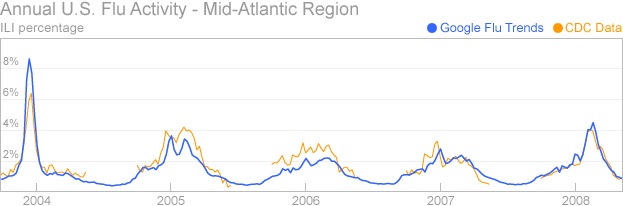
This graph shows five years of query-based flu estimates for the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, compared against influenza surveillance data provided by CDC’s U.S. Influenza Sentinel Provider Surveillance Network. As you can see, estimates based on Google search queries about flu are very closely matched to a flu activity indicator used by CDC. Of course, past performance is no guarantee of future results. Our system is still very experimental, so anything is possible, but we’re hoping to see similar correlations in the coming year.
CDC uses a variety of methods to track influenza across the United States each year. One method relies on a network of more than 1500 doctors who see 16 million patients each year. The doctors keep track of the percentage of their patients who have an influenza-like illness, also known as an “ILI percentage”. CDC and state health departments collect and aggregate this data each week, providing a good indicator of overall flu activity across the United States.
So why bother with estimates from aggregated search queries? It turns out that traditional flu surveillance systems take 1-2 weeks to collect and release surveillance data, but Google search queries can be automatically counted very quickly. By making our flu estimates available each day, Google Flu Trends may provide an early-warning system for outbreaks of influenza.
For epidemiologists, this is an exciting development, because early detection of a disease outbreak can reduce the number of people affected. If a new strain of influenza virus emerges under certain conditions, a pandemic could emerge and cause millions of deaths (as happened, for example, in 1918). Our up-to-date influenza estimates may enable public health officials and health professionals to better respond to seasonal epidemics and — though we hope never to find out — pandemics.